Medical Image Encryption Using Edge Maps
Introduction
This paper presents a medical image encryption algorithm using edge maps derived from a source image. The algorithm is composed by three parts: bit-plane decomposition, generator of random sequence, and permutation. It offers users the following flexibilities: (1) any type of images can be used as the source image; (2) different edge maps can be generated by various edge detectors and thresholds; (3) selection of appropriate bit-plane decomposition method is flexible; (4) many permutation methods can be cascaded with the proposed algorithm. A significantly large key space and strong key sensitive are possessed by the proposed algorithm to protect different types of medical images. Furthermore, it has a wider applicability than other methods for fuzzy edge maps. The histograms of the cipher-images are approximately flat even with blurry edge maps, which verify EMMIE possessing a strong robustness for fuzzy edge maps by the simulation results. The analysis of security demonstrates EMMIE is a secure algorithm. Source image, edge detector, and the parameters of scrambling method compose the keys of EMMIE and their combinations are significantly large to defend the Bruce-force attack. To further evaluates the security level of EMMIE, as is shown in the comparisons with other state-of-the-art methods, EMMIE possesses a higher pixel correlation, stronger key sensitivity and error robustness, and a better performance against differential attack with less time cost.
Main results
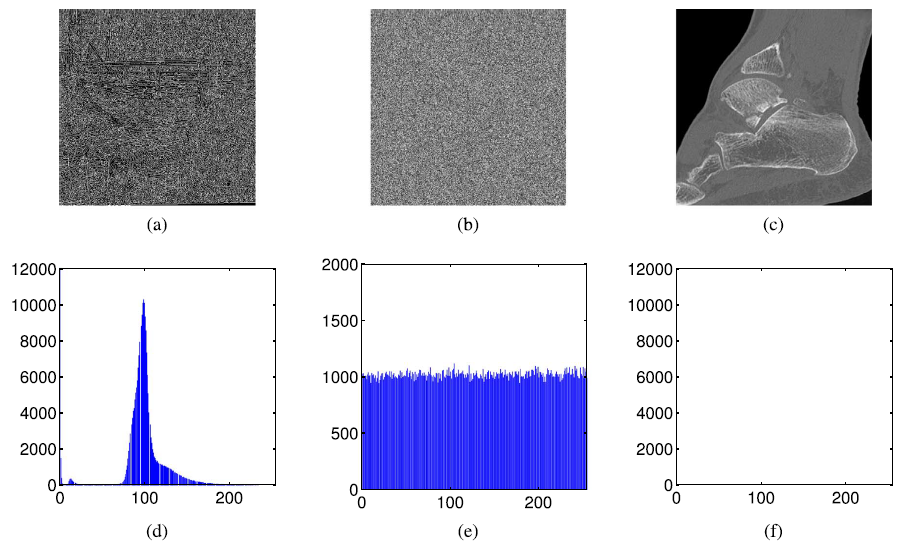 |
EMMIE encryption results of the CT image: (a) The edge map extracted from Fig. 3 (q) (Sobel detector); (b) the cipher-image; (c) the reconstructed CT image; (d) the histogram of the original image shown in the Fig. 3(p); (e) the histogram of (b); (f) the histogram of the difference between the original image and (c).
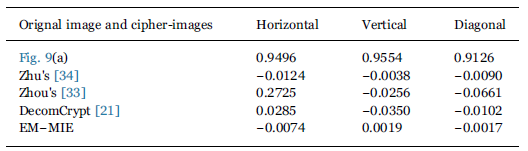 |
| Correlation coefficients of the original image shown in the Fig. 9(a) and cipher-images using different encryption algorithms. |
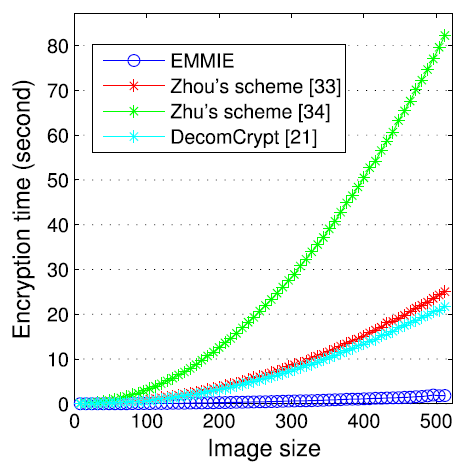 |
The encryption time of the schemes of Zhu, Zhou, DecomCrypt and EMMIE with the increasing size of the original image in Fig. 3(l). The green, red, blue-green and blue lines represent the methods of Zhu, Zhou, DecomCrypt and EMMIE, respectively.
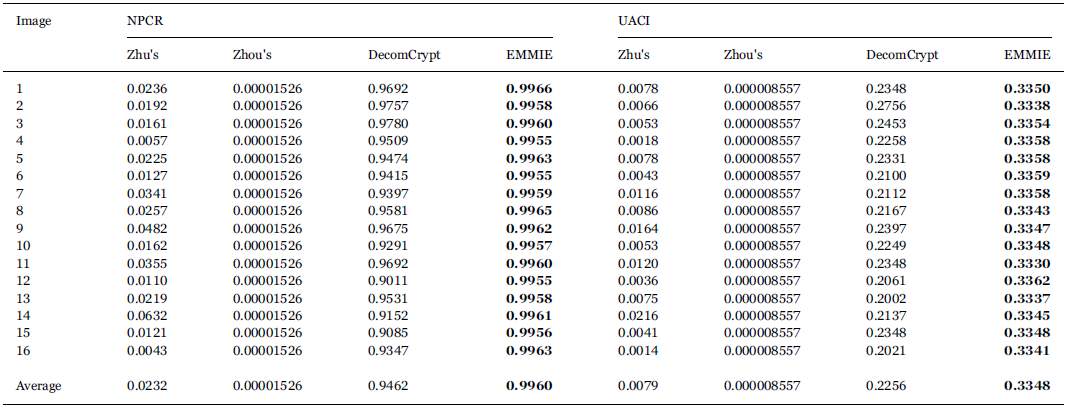 |
| NPCR and UACI results of different encryption algorithms. |